
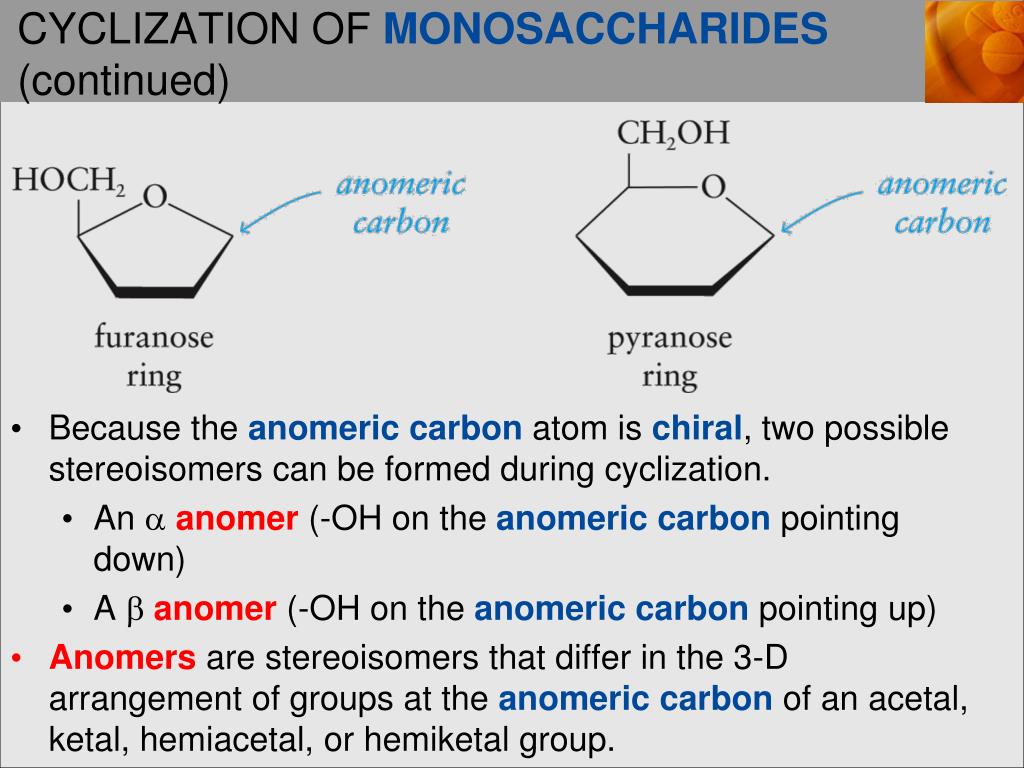
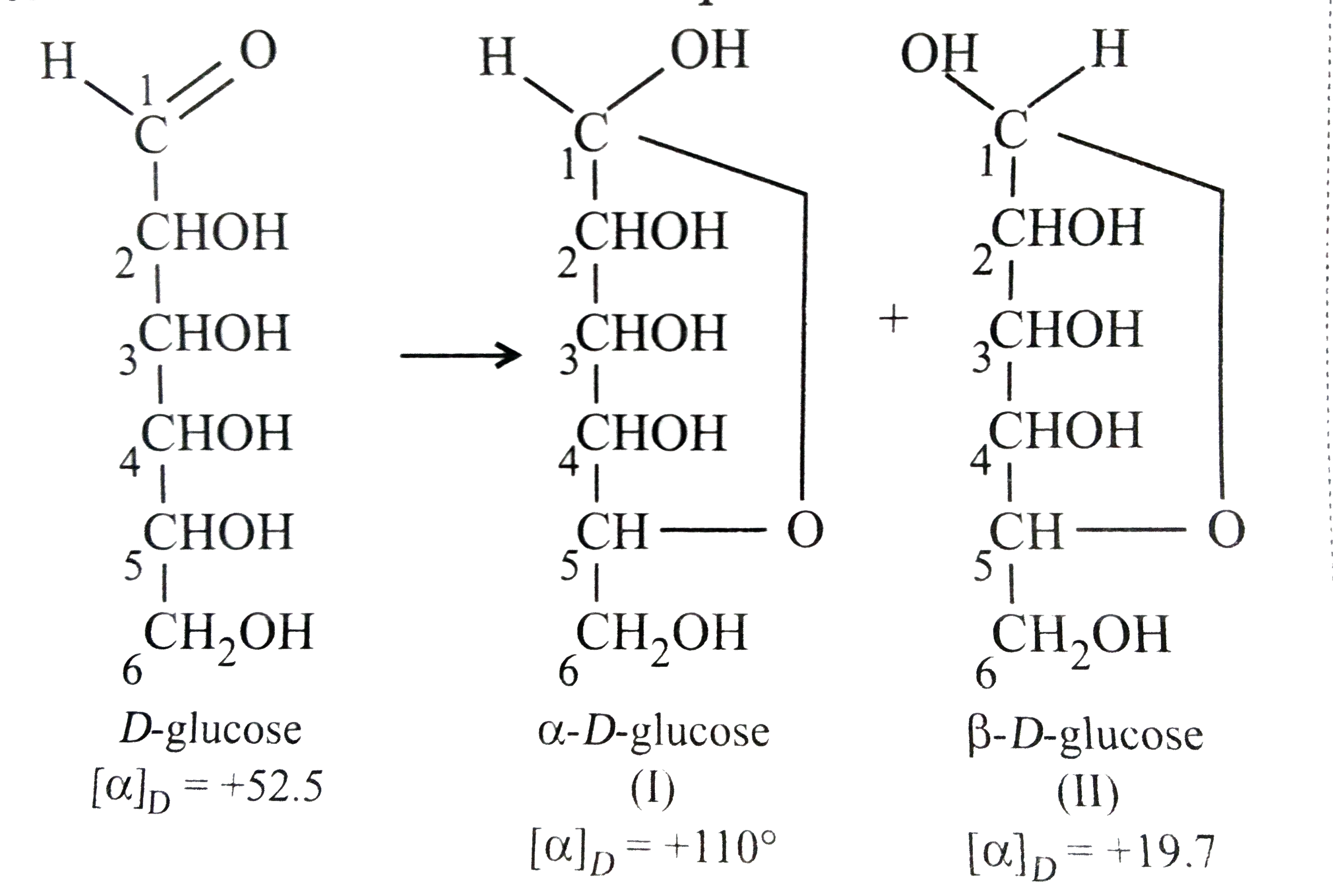
The carbon (C) connected to two oxygen (O) atoms joined by single bonds determines the anomeric carbon. Or The carbon in a monosaccharide (such as glucose) that rotates is an example of anomeric carbon. One might wonder why such branching occurs more abundantly in animals than in plants. The carbonyl group in D-fructose is at C2. Glycogen, however, has many more alpha 1-6 branches than amylopectin, with such bonds occurring about every 10 residues. Glycogen is a polysaccharide that is physically related to amylopectin in being built only of glucose and in having a mix of alpha 1-4 and alpha 1-6 bonds. Individuals with I-cell disease suffer developmental delays, abnormal skeletal development, and restricted joint movement. 1, forms a cyclic structure, the carbonyl oxygen atom may be pushed either up or down, giving rise to two stereoisomers, as shown. When a straight-chain monosaccharide, such as any of the structures shown in Figure 16.4.1 16.4. In the absence of a functioning enzyme, the unphosphorylated glycoprotein never makes it to the lysosome and is instead exported out of the cell where it accumulates in the blood and is excreted in the urine. By reacting the OH group on the fifth carbon atom with the aldehyde group, the cyclic monosaccharide (c) is produced.

This enzyme normally catalyzes the addition of a phosphate to a mannose sugar attached to a protein destined for the lysosome. Furthermore, fructose belongs to the ketoses while glucose is from the aldoses family. Unlike glucose, it forms five-membered ringed cyclic hemiacetals (in case of pyranoses) with anomeric carbon at C-2. For example, inclusion cell (I-cell) disease arises from a defective phosphotransferase in the Golgi. Fructose is the sweetest sugar of all, also called ‘levulose’ and ‘fruit sugar’ is usually found in honey, corn syrup, sweet fruits, etc.
Improper glycosylation or sugar modification patterns can result in the failure of proteins to reach the correct cellular compartment. The linkage joins carbon atom 1 (in the configuration) of one glucose molecule and carbon atom 4 of the second glucose molecule the linkage may also be abbreviated -1, 4. Therefore, some copper(II) complexes were prepared. The oligosaccharides that are attached to proteins may also determine their cellular destinations. Representative disaccharides and oligosaccharides. fructose re-draw anomeric carbon 1 CH 2 OH C O CH2OH O CH2OH OH CH2OH OH H H HO CH 2 OH OH H HO 2 H H H HO CH2 H OH OH H OH H OH anomeric carbon anomer O. from publication: Investigations of carbohydrate isomers and metal. The types of oligosaccharides found on the surface of blood cells is a determinant of blood type. On the cell surface, glycoproteins with distinctive oligosaccharides attached establish the identity of each cell. Oligosaccharides often function as identity markers, both of cells and proteins.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
